Identifying Thyroid Cancer Indicators
Introduction
Welcome to Thyroid Insights, your guide to understanding the signals your body may be sending. Discover a world where knowledge empowers, and awareness saves lives. In this realm of holistic wellness, we unveil the subtle cues, under which lies the truth about thyroid cancer symptoms. Let us embark on this enlightening journey, together.
Understanding Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer develops in the thyroid gland, a vital organ in the neck responsible for hormonal regulation. It’s categorized into types like papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic, each with unique characteristics. Understanding these types can help in recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.
Detailed Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
Recognizing the symptoms of thyroid cancer early can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Here are some common symptoms:
- Neck Changes: A lump or swelling in the neck is often the first noticeable symptom. It may be painless and gradually increase in size.
- Voice Changes: Unexplained hoarseness or voice changes that persist could be a sign of thyroid cancer affecting the vocal cords.
- Swallowing and Breathing Difficulties: A growing tumor may press against the windpipe or esophagus, causing trouble swallowing or breathing.
- Persistent Cough: A cough not associated with a cold or allergies, especially if it’s persistent and unexplained, should be evaluated.
- Throat Pain: Pain in the throat or neck that doesn’t go away can be a symptom.
- Symptoms of Metastasis: In advanced stages, symptoms like coughing up blood, bone pain, or neurological symptoms might occur, indicating the cancer has spread.
- Changes in Thyroid Function: Unusual weight gain or loss, heat intolerance, and abnormal heart rates can be signs of altered thyroid function.
- Ear Pain: Some patients may experience pain in their ears.
- Enlarged Lymph Nodes: Swollen lymph nodes in the neck can be a sign of thyroid cancer.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Persistent fatigue and weakness, which are nonspecific but can accompany cancer.
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can increase the risk of developing thyroid cance
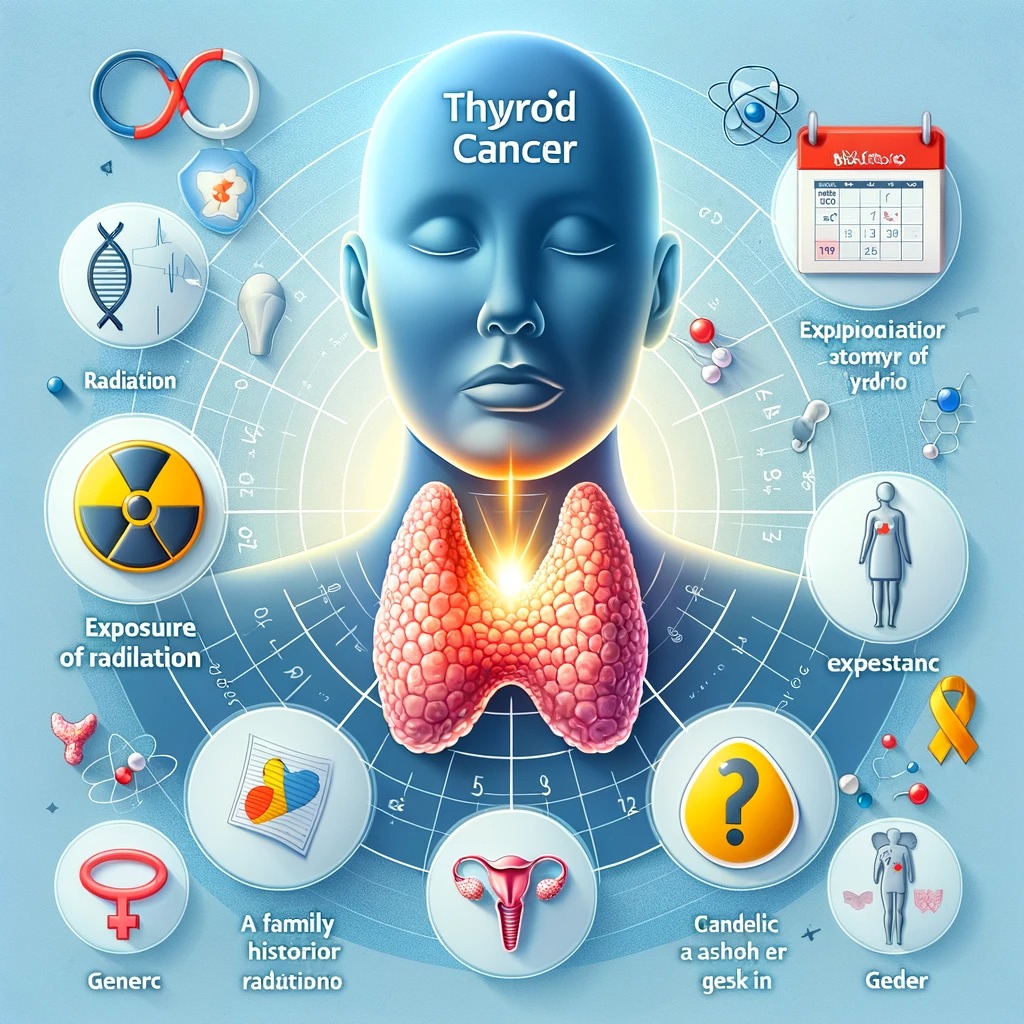
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of thyroid cancer or genetic conditions like familial medullary thyroid cancer increases risk.
- Gender and Age: Women are more likely to develop thyroid cancer, particularly between ages 40 and 60.
- Radiation Exposure: Exposure to high levels of radiation, especially during childhood, is a significant risk factor. This includes radiation therapy for other cancers.
- Dietary Factors: A diet low in iodine can increase risk, though this is more common in countries where iodine isn’t added to salt.
- Hormonal Factors: A history of goiter or thyroid nodules can increase risk, as can hormonal imbalances.
- Environmental Influences: Exposure to certain chemicals or pollutants may contribute to the risk of thyroid cancer.
Understanding these risk factors is crucial for early detection and prevention strategies.
Diagnosis and Screening
Diagnosing thyroid cancer typically involves several steps
- Physical Examination: A doctor will feel the neck for lumps or abnormalities in the thyroid gland.
- Blood Tests: Tests to evaluate thyroid function, including measuring levels of thyroid hormones and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound of the neck can visualize the thyroid gland and identify nodules or tumors.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy: If a nodule is found, a biopsy may be performed to determine if it’s cancerous. This involves extracting a sample of cells from the nodule.
- Imaging Tests: Additional imaging tests like CT scans, MRIs, or PET scans may be used to determine the extent of the cancer and if it has spread.
- Genetic Testing: In cases with a family history of thyroid cancer, genetic testing may be recommended to assess risk.
Early and accurate diagnosis is key to effective treatment and better outcomes.
NIFI Technology in Surgical Treatment
At www.thethyroidcancer.clinic, NIFI Technology is used in thyroid cancer surgeries. This innovative approach
Precision Oncology for Thyroid Cancer Treatment
- Precision oncology at www.thethyroidcancer.clinic involves tailoring treatment based on individual patient profiles. This approach ensures targeted and effective treatment strategies.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Cancer
- Effective treatment of thyroid cancer depends on the type and stage of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences. Here are the primary treatment options:
Surgery
Surgery is the most common treatment for thyroid cancer and can involve:
- Total Thyroidectomy: Removal of the entire thyroid gland. This is often recommended if cancer is found in more than one part of the thyroid or if there is a risk of cancer recurrence.
- Lobectomy: Removal of only one lobe of the thyroid. This might be considered if the cancer is small and confined to one lobe.
- Lymph Node Removal: If cancer has spread to lymph nodes in the neck, these may also be removed during surgery.
Post-surgery, patients may require thyroid hormone replacement therapy since the thyroid gland’s hormone-producing ability is reduced or eliminated.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
After thyroid surgery, radioactive iodine therapy may be used to destroy any remaining thyroid tissue or cancer cells. This treatment takes advantage of the fact that thyroid cells naturally absorb iodine. The patient ingests radioactive iodine in liquid or capsule form, which then selectively targets and destroys thyroid cells.
Hormone Therapy
Patients who undergo total thyroidectomy will need lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy. This not only compensates for the loss of the thyroid gland but also helps suppress the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland, which can stimulate the growth of any remaining cancer cells.
Targeted Drug Therapy
Targeted drug therapies focus on specific abnormalities present within cancer cells. By blocking these abnormalities, targeted drug treatments can cause cancer cells to die. This is particularly useful in treating advanced thyroid cancers that don’t respond to radioactive iodine therapy.
External Radiation Therapy
This treatment uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays or protons, to kill cancer cells. External beam radiation therapy is typically used when cancer has spread beyond the thyroid and cannot be treated with surgery or radioactive iodine therapy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells and is generally used when thyroid cancer is unresponsive to other treatments. It’s more commonly used for anaplastic thyroid cancer, which is less responsive to other forms of treatment.
Clinical Trials
Participating in clinical trials can provide access to new and innovative treatments for thyroid cancer. Patients interested in clinical trials should discuss this option with their healthcare provider.
Follow-Up and Long-Term Care
Regular follow-up care is essential after thyroid cancer treatment. This includes periodic blood tests to monitor thyroid hormone levels and check for signs of cancer recurrence, as well as imaging tests as recommended by the healthcare provider.
Patient Support and Resources
Support groups and counseling can be invaluable for patients and families. Resources for support and information include healthcare providers, patient advocacy groups, and online resources.
Lifestyle and Holistic Approaches
Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, can support overall well-being. Holistic practices like yoga and meditation may help manage stress and improve quality of life during and after treatment.

Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of thyroid cancer is the first step toward timely and effective treatment. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
About
www.thethyroidcancer.clinic is dedicated to providing advanced care for thyroid cancer, utilizing NIFI Technology and precision oncology to offer the best possible outcomes for our patients.